
What’s Behind the Unusual Spike in Malware Indicators in April?
May 4, 2023
PART 1 of 2. We continue to publish statistical materials on the threats that have caught our attention over the past month. This article will be divided into two parts since April was rich in such threats. Previous publications can be viewed here.
Malware is an ever-evolving threat in the world of cybersecurity, with new variants and updates appearing frequently. In the past month alone, several malicious software programs have captured the attention of our threat intelligence experts due to their increased indicators of compromise.
Thees are some of the malware types that have seen a noticeable, but systematic rise in indicators, including April:
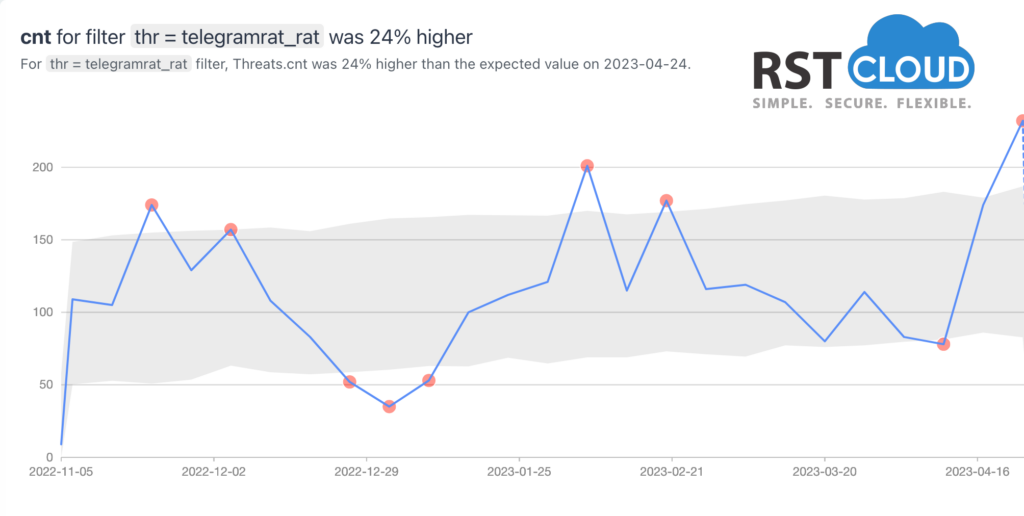
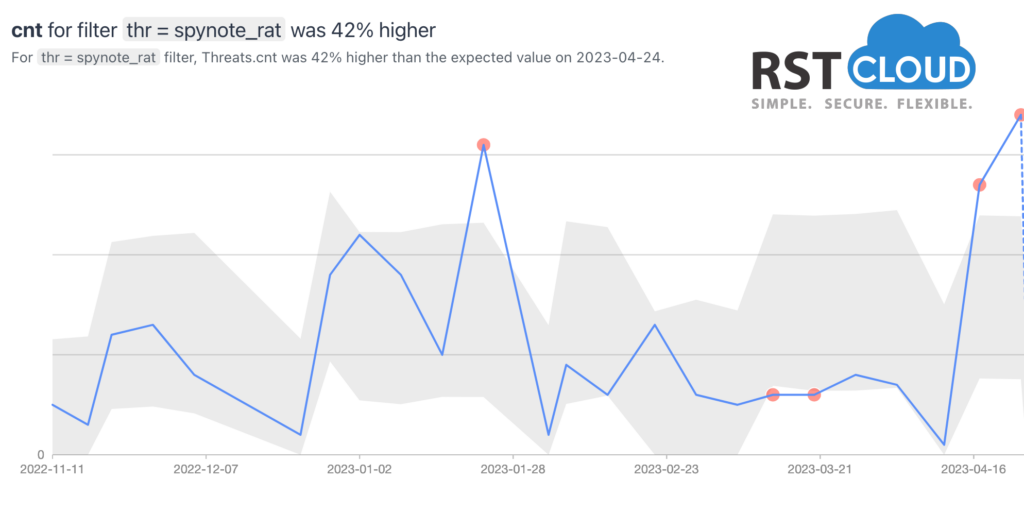
- Android Spyware Telegram RAT and Spynote RAT
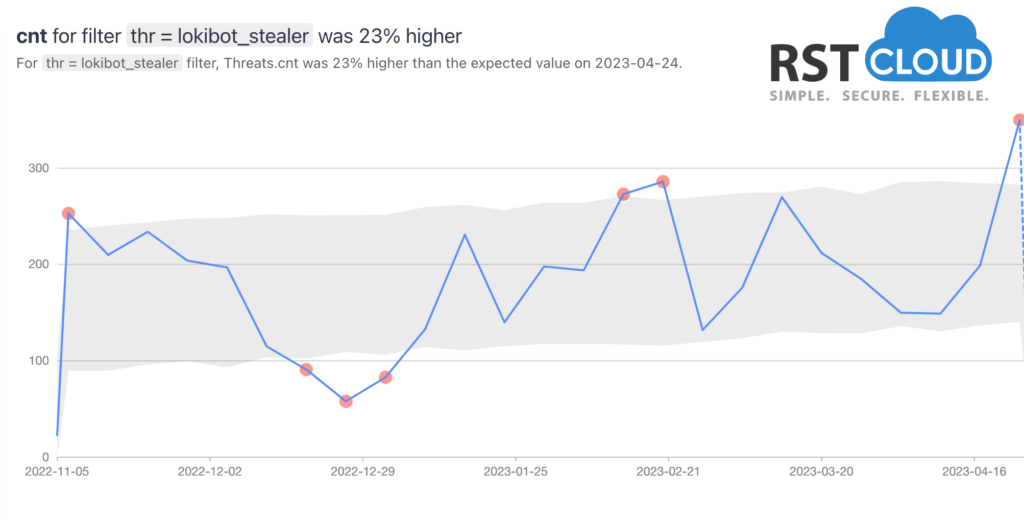
- Lokibot and Stormkitty Stealer
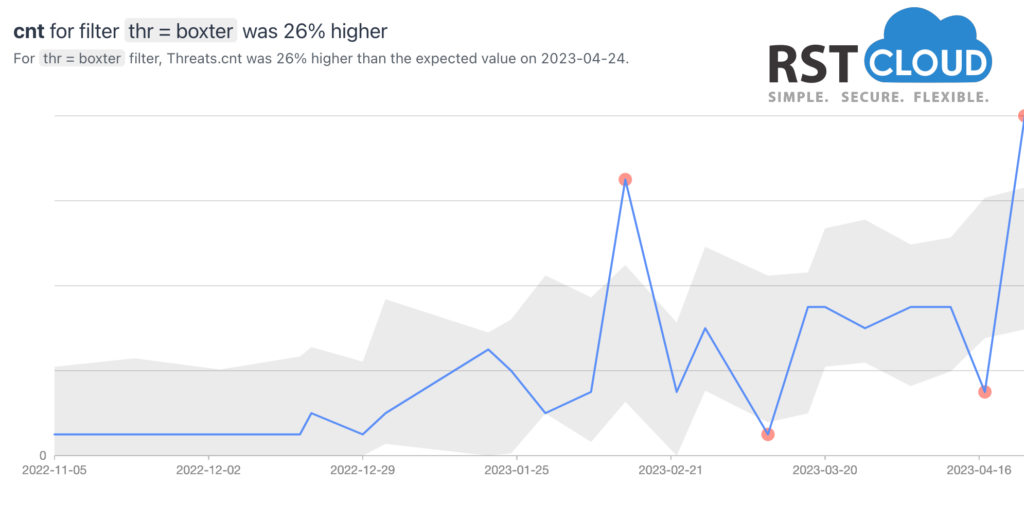
- Boxter Trojan
- Privatloader.
However, even more alarming is the huge anomalous surge in threats such as:
- Shifu,
- NetWire, Gh0st and Xrat RAT,
- Pony and BluStealer,
- Masscan Ransomware.
Let’s take a closer look at these malware types and their potential impact on individuals and organizations.
Attackers frequently employ Android Spyware to gain access to personal data and carry out fraudulent activities. This malware is capable of tracking a user’s location, monitoring web browsing patterns, and stealing sensitive information such as credit card numbers and passwords. Spyware can also exploit legitimate APIs and permissions intended for user assistance to record phone calls, intercept SMS messages, remotely manage devices, and perform other tasks.
A Telegram RAT for Android, known as Spying Capability Malware, can pilfer confidential information from Android users through the message-exchange protocol of the Telegram online messenger. SpyNote RAT is another type of malicious Android app that utilizes a builder tool to create malevolent apps with malware functionalities. SpyNote RAT’s popularity stems from its free use, allowing anyone to distribute their version, and experienced criminals can develop additional modules to extend its features.
LokiBot is one of the most prevalent and hazardous malware today. Analysis of LokiBot malware reveals that it employs a keylogger to monitor the victim’s desktop and browser activities, allowing hackers to access usernames, passwords, bank details, cryptocurrency wallet contents, and other personal data. It can also disable notifications, intercept communications, and act as a backdoor for installing additional payloads and carrying out other malicious actions. Moreover, the latest version of LokiBot incorporates multiple layers of encryption, making it harder to detect.
Due to its ease of implementation and high efficacy in causing damage, LokiBot is a favored malware tool for cybercriminals, including those with limited technical skills or those new to cybercrime. Its accessibility on underground forums is another factor contributing to its popularity.
Boxter Trojan is a type of malware that is designed to remain hidden on an infected system while gathering sensitive information. It is known for its stealthy behavior, which makes it difficult to detect by traditional antivirus software.
Boxter Trojan infiltrates a system either as a file that is dropped by other malware or as a file that is unwittingly downloaded by users while visiting malicious websites. Once installed, it collects various types of data, such as the Mac address, operating system version, installed antivirus, domain, and username.
Boxter Trojan is often spread through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or by exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems. Once it gains access to a system, it can quickly spread to other computers on the same network, making it even more difficult to contain.
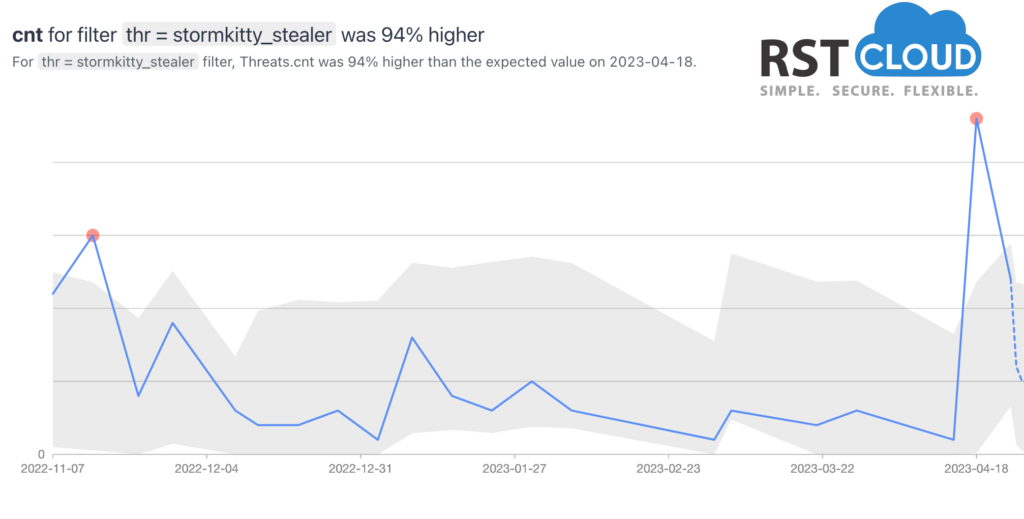
StormKitty is an open-source information stealer that has a range of functions for stealing data from a victim’s computer. This malware is designed to be stealthy and can capture various sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal identification data. StormKitty can be spread through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or by exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems.
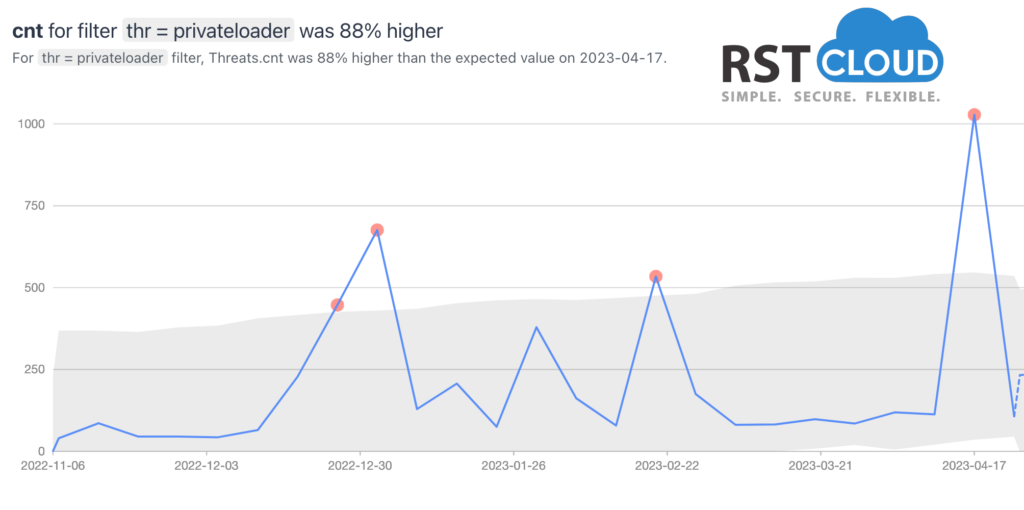
PrivateLoader was one of the most widely used loaders in 2022, and is used by a Pay-Per-Install (PPI) service to deploy multiple malicious payloads on infected hosts. PPI is a malware service that monetizes the installation of malicious software. A malware operator provides a PPI service operator with a payload, requested number of installations, and target location.
PrivateLoader is a modular malware that downloads and executes one or more payloads, implementing anti-analysis techniques and reporting statistics to its C2 server. Individuals who sell “installs” have a significant impact on the spread of malicious software and the underground economy.
To be continued..